Primary prevention
- Sanitation : Safe disposal of human excreta coupled with elementary sanitation practice i.e. washing hands after the sanitation and washing hands before and after meals.
- Water supply : The protection of water supply against faecal contamination.
- Food hygiene : Food should be protected against faecal contamination. Vegetable and fruits can be disinfected with aqueous solution of vinegar.
- Health education and public awareness.
Secondary prevention
Early diagnosis : Demonstration of trophozoites containing red cell is diagnostic. Readily seen in fresh mucus passed per rectum. Microscopy should be performed immediately before its complication result. The absence of pus cells in stool may be helpful in differential diagnosis.
Treatment : In symptomatic case – Metronidazole orally in 30 mg/kg of body weight, divided in 3 doses after meals for 8-10 days.
LIFE CYCLE OF ENTAMOEBA HISTOLYTICA
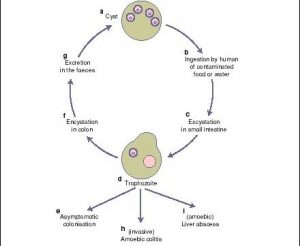
E.histolytica passes its life cycle only in one host : man. There are mainly 2 phases of development – trophozoite and cyst with a transitory stage of the pre-cystic form. The mature quadric-mucleate cysts are infective forms of parasite. When these cysts are swallowed along with the contaminated food and drinks by a susceptible person, they are capable of further development inside the gut. The cyst wall is resistant to action of gastric juice but is digested by the action of trypsin in the intestine. The ex-cystation occurs when the cyst reaches the caecum, at the lower part of ileum. Each cyst liberate a single amoeba with 4 nuclei, a tertanucleate amoeba which eventually form 8 amoebulae by the division of nuclei with successive fusion of cytoplasm.
During growth, E.histolytica secrete a proteolytic ferment of mature histolytica which bring about destruction and meiosis of tissue and thereby helps the parasite in obtaining nourishment through absorption of these dissolved tissue juices.
If the parasite happens to enter a resistant host, the injuries produced are minimal. These persons are those who act as a constant source of infection to others.