VISIT TO CHANDRAWAL WATER TREATMENT PLANT
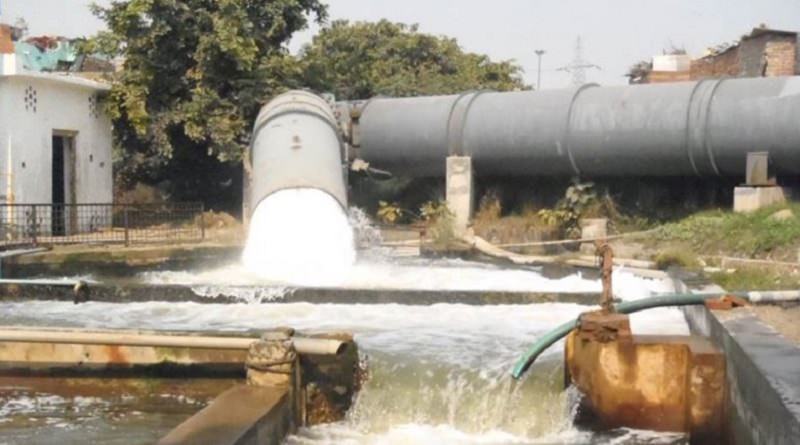
The Chandraval water treatment plant is the biggest plant in India. Raw water is made suitable here for various domestic purposes. The plant received 650 million gallon of water per day. This much quantity of water is received from various sources : ground water, surface water, Yamuna river, Gange’s surface. Water is treated at Wazirabad, Hyderpur, Nangloi and Okhla plants. Ground water is simply chlorinated and a plant part is treated at Okhla. Here water is checked at every step of process. So, this water treatment works for 24 hours, on all days. The whole process includes :
- Pre-chlorination : Chlorine demand of raw water is estimated, which is about 4.2 ppm. Chlorine cylinder of 900 kg (PACL) containing chlorine in liquid form is attached for chlorination as a source of chlorine.
- Alum treatment : Ferric alum is used.
Dose estimated from lab – 35 ppm
Poly aluminium chloride (PAC) solution is also used for treatment of water. It is available in liquid form. 50% less dose is required as compared to alum.
Dose : 150 ml in 30 sec, PAC is added.
- Flocculation : Water and alum are flocculated for 3 minutes.
- Sedimentation : 6 sedimentation tanks are used. 2 tanks of 7.5 MGD, 4 tanks of 10 MGD capacity where 62 MGD of water is treated.
Retention period of water : 2-15 minutes
Bludge movement : 45 minutes
- Filteration : 31 filters of 2 MGD capacity are used.
- Post-chlorination : 1.5 ppm of chlorine at domestic level.
- Send to reservoir.
LABORATORY
Here following tests are done –
- Chlorine estimation
- Alkalinity
- pH and turbility
- Alum and PAC
- Chloride
- DO : Dissolved oxygen
- OA : Oxygen absorption
- Residual alumina
IMPURITIES IN WATER
Water pollution agent
Natural impurities Man-made impurities
- Dissolved gases eg. Nitrogen a. sewage
carbon dioxide, hydrogen sulphide
- Dissolved salts eg. salts of b. Agricultural waste
calcium, sodium, magnesium
- Suspended impurities eg. day c. Physical pollutants i.e. heat
salt, sand, mud. Radioactive substance
- Micro-organisms d. Industrial waste
INDICATORS OF POLLUTION
- Amount of total suspended colloid.
- Biochemical oxygen demand at 20oC.
- Concentration of chlorides, nitrogen, phosphorus.
- Absence of dissolved oxygen.
WATER TREATMENT
The water which is treated at the water treatment plant is not pure. It contains various impurities like minerals, dissolved gases, suspended impurities etc. This contaminated water is very injurious to our health so it is necessary to treat this contaminated water, to make it usable. Chlorination of water is one of the greatest advancement in water purification. Chlorine kills pathogenic bacteria, oxidises iron, magnesium and hydrogen sulphide.
The acceptability of water can be influenced by many constituents. Water is diagnosed in relation to these aspects –
- Turbidity : It can interfere with disinfection. Water with turbidity less than 5 NTU is usually acceptable. Turbidity is due to particulate matter.
- Colour : Drinking water should be free from colour that may be due to colored organic matter, metals such as iron, manganese, etc.
- pH : The acceptable pH of drinking water is between 6.5 – 8.5 pH level below 7 may cause corrosion of metal in distribution pipes. pH above 8 causes decrease in the affinity of chloride process.
- Chloride : Standard level is 200 mg/L.
RAPID SAND OR MECHANICAL FILTER
Rapid sand filters were first installed in 1885 in USA. They are of 2 types-
– Gravity type
– Pressure type
Following steps are there in Rapid Sand Filteration –
- Coagulation : The raw water is treated with alum, the dose of which varies from 5-40 mg or more per litre, depending upon turbidity, colour.
- Rapid mining : The treated water is agitated in mining chamber for few minutes. It is for thorough dissemination of alum throughout the bulk of water.
- Flocculation : This phase involves the treatment of water in flocculation chamber. This is done for about 20 min. Mechanical type of flocculation is mostly used, consists of rotating paddles. It results in formation of copious, thick white flocculent precipitates of aluminium hydroxide.
- Sedimentation : Here the coagulated water is kept for a period of few hours, so that precipitate together with impurities and bacteria, settle down in the tank. The precipitates which settle down, are removed simultaneously.
- Filteration : The partly clarified water is now subjected to filteration.
FILTER BEDS
Each unit of filter bed has a surface of about 80-90m2, sand as filterating medium and depth of sand bed is about 1 mtr. Then there is a layer of graded gravel which permits the filtered water to move freely towards the under drain that collects the filtered water. The rate of filteration is 5-15 m3/m2/hr. The ‘alum floc’ not removed by sedimentation is held back on sand bed.
BACK WASHING
When filteration is stopped due to blockage, filters are subjected to washing process. This process is known as back washing. This is brought about by reversing the flow of water. When clean sand is rising, washing is stopped. Back washing process cleans up the sand bed. The process takes up about 15 minutes.
ADVANTAGES
- Raw deal with raw water directly
- Filter bed occupy less space
- Rapid filteration
- Washing of filter is easy
- Flexibility in operation
- Chlorination – Chlorine isn’t a substitute but supplement to sand filteration. It kills bacteria but has no effect on spores, virus, cyst, ova, helminth etc. It oxidizes oxygen, iron, manganese, hydrogen sulphide. It destroys taste and odour producing substances.
Action
H2O + Cl2 HCl + HOCl
(Water) (Chlorine) (Hypochlorous acid)
Hydrochlorous acid is neutralized by alkalinity of water.
HOCl H+ + OCl-
Hypochlorous Hydrogen Hypochlorous
Acid ion ion
Disinfection is due to –
- Hypochlorous acid
- Hypochlorous ion
Chlorine acts best at pH 7 and it can be applied as –
- Chlorine gas
- Chloramines
- Perchloron
- admin |
- December 4, 2021